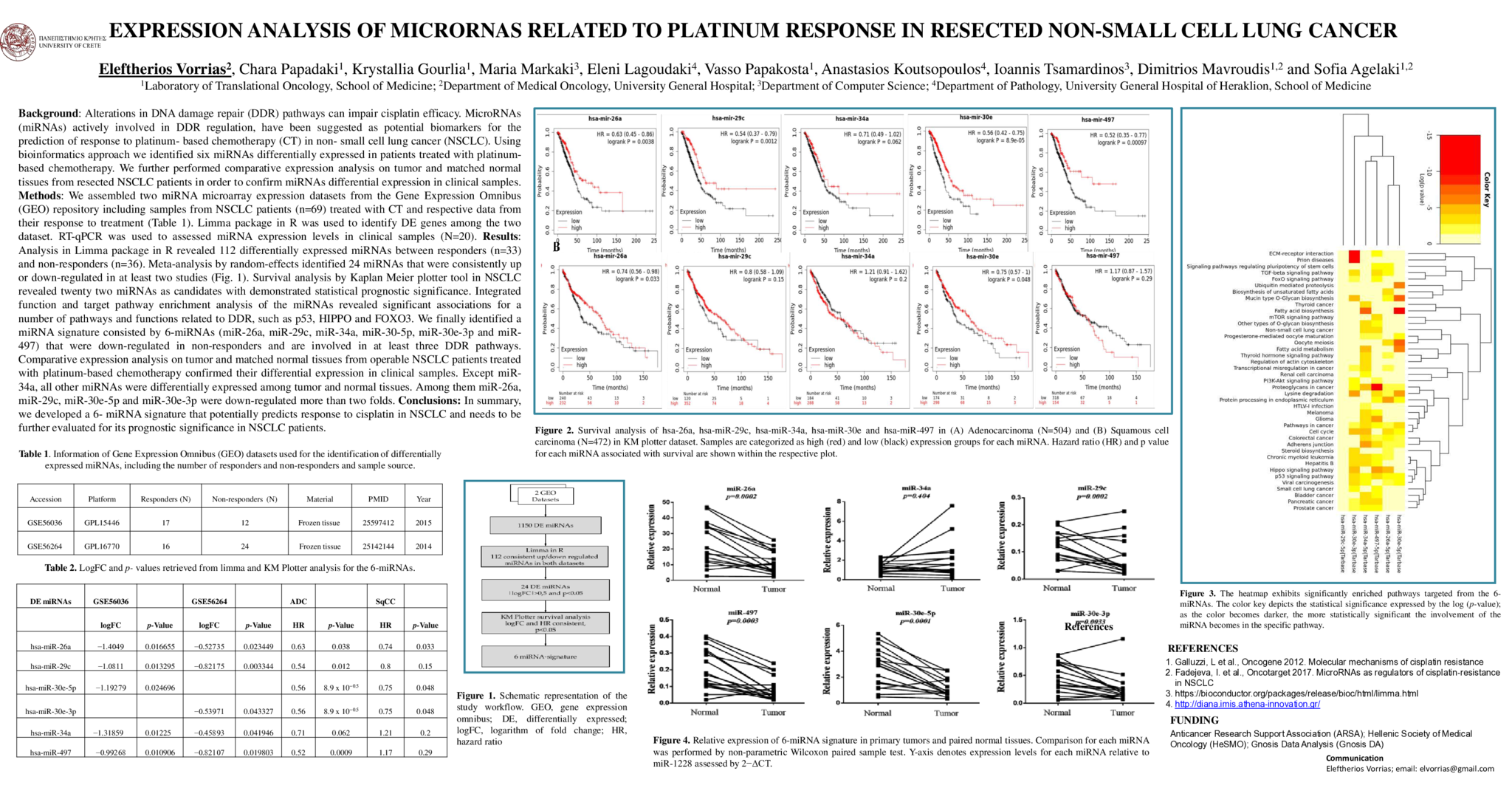
Background: Alterations in DNA damage repair (DDR) pathways can impair cisplatin efficacy. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) actively involved in DDR regulation, have been suggested as potential biomarkers for the prediction of response to platinum- based chemotherapy (CT) in non- small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Using bioinformatics approach we identified six miRNAs differentially expressed in patients treated with platinum-based chemotherapy. We further performed comparative expression analysis on tumor and matched normal tissues from resected NSCLC patients in order to confirm miRNAs differential expression in clinical samples.
Methods: We assembled two miRNA microarray expression datasets from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) repository including samples from NSCLC patients (n=69) treated with CT and respective data from their response to treatment. Limma package in R was used to identify DE genes among the two dataset. RT-qPCR was used to assessed miRNA expression levels in clinical samples (N=20).
Results: Analysis in Limma package in R revealed 112 differentially expressed miRNAs between responders (n=33) and non-responders (n=36). Meta-analysis by random-effects identified 24 miRNAs that were consistently up or down-regulated in at least two studies. Survival analysis by Kaplan Meier plotter tool in NSCLC revealed twenty two miRNAs as candidates with demonstrated statistical prognostic significance. Integrated function and target pathway enrichment analysis of the miRNAs revealed significant associations for a number of pathways and functions related to DDR, such as p53, HIPPO and FOXO3. We finally identified a miRNA signature consisted by 6-miRNAs (miR-26a, miR-29c, miR-34a, miR-30-5p, miR-30e-3p and miR-497) that were down-regulated in non-responders and are involved in at least three DDR pathways. Comparative expression analysis on tumor and matched normal tissues from operable NSCLC patients treated with platinum-based chemotherapy confirmed their differential expression in clinical samples. Except miR-34a, all other miRNAs were differentially expressed among tumor and normal tissues. Specifically, miR-26a, miR-29c, miR-30e-5p, miR-30e-3p and miR-497 were down-regulated in tumor tissues. Among them miR-26a, miR-29c, miR-30e-5p and miR-30e-3p were down-regulated more than two folds.
Conclusions: In summary, we developed a 6- miRNA signature that potentially predicts response to cisplatin in NSCLC and needs to be further evaluated for its prognostic significance in NSCLC patients.
- 4 προβολές