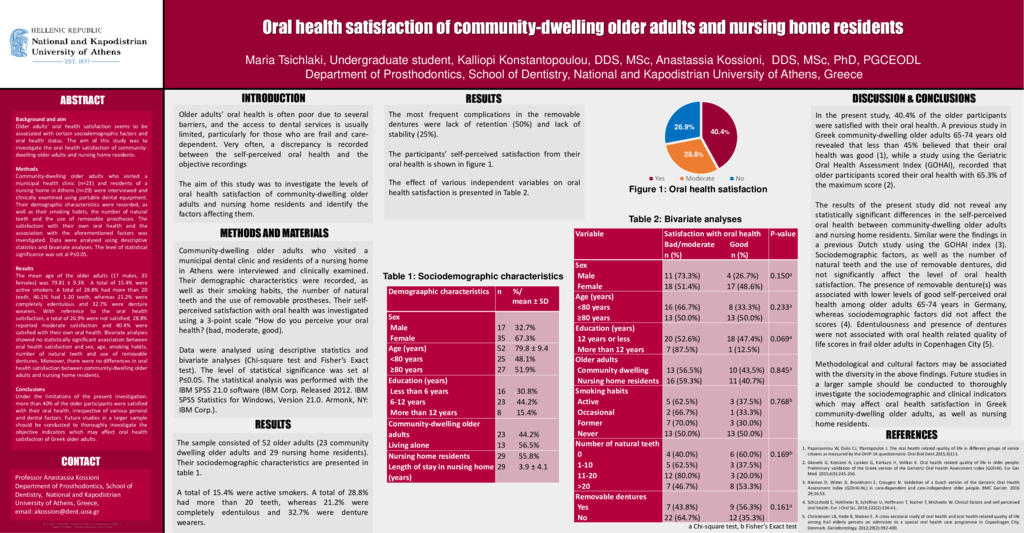
Background and aim: Older adults’ oral health satisfaction seems to be associated with certain sociodemographic factors and oral health status. The aim of this study was to investigate the oral health satisfaction of community-dwelling older adults and nursing home residents. Methods: Community-dwelling older adults who visited a municipal health clinic (n=23) and residents of a nursing home in Athens (n=29) were interviewed and clinically examined using portable dental equipment. Their demographic characteristics were recorded, as well as their smoking habits, the number of natural teeth and the use of removable prostheses. The satisfaction with their own oral health and the association with the aforementioned factors was investigated. Data were analysed using descriptive statistics and bivariate analyses. The level of statistical significance was set al P≤0.05. Results: The mean age of the older adults (17 males, 35 females) was 79.81 ± 9.39. A total of 15.4% were active smokers. A total of 28.8% had more than 20 teeth, 46.1% had 1-20 teeth, whereas 21.2% were completely edentulous and 32.7% were denture wearers. With reference to the oral health satisfaction, a total of 26.9% were not satisfied, 28.8% reported moderate satisfaction and 40.4% were satisfied with their own oral health. Bivariate analyses showed no statistically significant association between oral health satisfaction and sex, age, smoking habits, number of natural teeth and use of removable dentures. Moreover, there were no differences in oral health satisfaction between community-dwelling older adults and nursing home residents. Conclusions: Under the limitations of the present investigation, more than 40% of the older participants were satisfied with their oral health, irrespective of various general and dental factors. Future studies in a larger sample should be conducted to thoroughly investigate the objective indicators which may affect oral health satisfaction of Greek older adults.
- 81 views